[ad_1]
Threat hunters have discovered a new Linux malware called GTPDOOR that’s designed to be deployed in telecom networks that are adjacent to GPRS roaming exchanges (GRX)
The malware is novel in the fact that it leverages the GPRS Tunnelling Protocol (GTP) for command-and-control (C2) communications.
GPRS roaming allows subscribers to access their GPRS services while they are beyond the reach of their home mobile network. This is facilitated by means of a GRX that transports the roaming traffic using GTP between the visited and the home Public Land Mobile Network (PLMN).
Security researcher haxrob, who discovered two GTPDOOR artifacts uploaded to VirusTotal from China and Italy, said the backdoor is likely linked to a known threat actor tracked as LightBasin (aka UNC1945), which was previously disclosed by CrowdStrike in October 2021 in connection with a series of attacks targeting the telecom sector to steal subscriber information and call metadata.
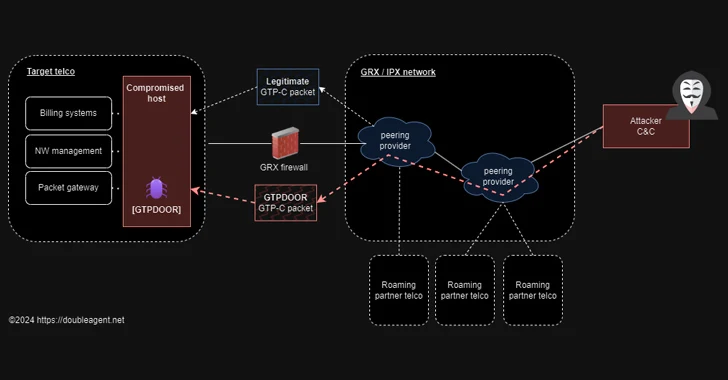
“When run, the first thing GTPDOOR does is process-name stomps itself – changing its process name to ‘[syslog]’ – disguised as syslog invoked from the kernel,” the researcher said. “It suppresses child signals and then opens a raw socket [that] will allow the implant to receive UDP messages that hit the network interfaces.”
Put differently, GTPDOOR allows a threat actor that already has established persistence on the roaming exchange network to contact a compromised host by sending GTP-C Echo Request messages with a malicious payload.
This magic GTP-C Echo Request message acts as a conduit to transmit a command to be executed on the infected machine and return the results back to the remote host.
GTPDOOR “Can be covertly probed from an external network to elicit a response by sending a TCP packet to any port number,” the researcher noted. “If the implant is active a crafted empty TCP packet is returned along with information if the destination port was open/responding on the host.”
“This implant looks like it is designed to sit on compromised hosts that directly touch the GRX network – these are the systems that communicate to other telecommunication operator networks via the GRX.”
[ad_2]