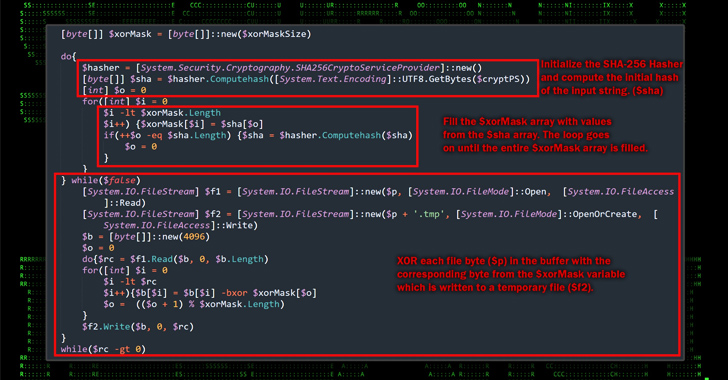
In television dramas and Hollywood movies, ransomware attacks are often made known by a flashy message that pops up on the computer screen or an ominous voice message left by the cyber criminal.
In the case of one hospital, the incident presented itself far more subtly.
Around 5:00 pm, the day after a holiday, calls started coming into the hospital’s IT team that an application was down. Then another. Followed by another.
Initially, the hospital’s IT team assumed they were dealing with a power issue and started investigating. It wasn’t until they stumbled upon the ransom note, hidden in a simple text file, that they realized their hospital had fallen prey to a ransomware attack.
Decisions, diversions, and disruptions
Because the team had no idea how widespread the attack was or what they were dealing with, they made the difficult but necessary decision to shut down all the hospital’s servers. In a non-hospital setting, this decision certainly isn’t easy, but in a hospital environment, it’s especially precarious as patient care and safety can be impacted.
What’s more is that shutting down systems often means that patients need to be diverted to other healthcare facilities, further disrupting care. While patient care was able to continue, it was in a delayed capacity. This slowdown also impacted the emergency department, leading to backlogs in their intake process.
Communications
Internal communication challenges compounded the situation. With the phone and email systems down, the primary methods that the hospital staff relied on to reach their colleagues, communication became difficult as few people had access to alternative phone numbers.
The stakeholders working to respond to the cyber attack established a command center to enable better communication and coordination. This helped them address multiple issues simultaneously, including contacting vendors, the cyber insurance provider, legal, and law enforcement.
Vendors
At the time of the incident, a third-party vendor hosted the hospital’s electronic medical records (EMR). To help preserve those records and protect the vendor, the IT team severed the connection and informed the EMR administrator. They also took similar actions for any other vendors connected to their systems.
Some vendors who were engaged to provide response and recovery assistance added an unexpected layer of complexity to the incident by wanting to focus on getting an updated contract in place before moving forward with support. Others, however, immediately provided the hospital with whatever help they needed, with a mutual agreement that a contract would be addressed to reflect the support once the hospital had gotten passed the incident.
Cyber Insurance
Initially, the hospital team was unable to get ahold of their cyber insurance provider. Due to their systems being down, they didn’t have access to the provider’s after-hours phone number. Fortunately, a few team members had the foresight to save some vendor contacts on their personal mobile devices and were able to connect with the cyber insurance provider and other vendors for assistance.
Once the cyber insurance provider got involved, they were able to use their expertise and resources to help the hospital team navigate the complex landscape of a ransomware incident and get them on the path to recovery.
Legal
The cyber insurance company also provided the hospital with a lawyer experienced in ransomware incidents and coordinating the nuanced communication components.
Something that surprised the IT team was the executive team’s direction to restore the phone system first. The team’s initial thought was to restore the EMR connection and other critical systems, but once the IT team synchronized with the executive leadership team, it became clear how critical accessible and streamlined communication is to a ransomware recovery effort.
In addition to keeping internal staff informed, it was imperative to communicate the situation effectively to the community and ensure that they could reach the hospital when necessary. To achieve this, the legal team collaborated with the hospital’s marketing and compliance departments to devise a communication and messaging strategy. The legal team also played a pivotal role in crafting response letters to vendors and handling any legal implications that arose during the incident.
Law enforcement
The hospital notified both the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) and local law enforcement about the incident. The FBI provided primary support for the hospital since most local law enforcement agencies lacked a cyber response team.
Ransomware attack lessons and learnings
Despite the challenges, the ransomware incident provided valuable opportunities for learning and growth, leading the hospital to adopt a much stronger cybersecurity posture.

Takeaway 1: Prepare for the worst, hope for the best
With healthcare ransomware attacks on the rise, it’s essential to accept the possibility that your hospital or health system will be impacted by one. By taking proactive measures to secure your defenses, and making your cybersecurity program a top priority within your organization, you’ll be in a stronger position to control the situation and successfully navigate the situation.
For example, conduct regular tabletop exercises. In cybersecurity, experts design tabletop exercises to mimic a real-life cybersecurity incident without affecting the organization’s live systems. The objective is to help organizations assess and improve incident response and cybersecurity readiness.
Involving the entire organization in incident response and recovery planning is imperative. Ransomware incidents impact the entire organization, and a collaborative approach ensures a coordinated and swift response.
Takeaway 2: Understand the scope and scale of your cybersecurity insurance
Cyber insurance goes beyond financial assistance, offering expertise, guidance, and resources that can prove invaluable during a crisis. It’s also likely that your cyber insurance provider will be of more assistance than you might realize. To avoid duplicating efforts and save time, know what your cyber insurance covers. This insight will help you focus on identifying gaps that your internal team or partners need to address.
Takeaway 3: Have backups for your backups
Don’t underestimate the importance of having backup systems in place and maintaining up-to-date documentation. Backup systems should be comprehensive and regularly tested to ensure reliability.
For example, having a non-electronic backup of vendor and staff contact lists is an often-overlooked aspect of incident response. Creating this list, maintaining it, and ensuring that it’s easily accessible can help ensure communication channels remain open during incidents, even when digital systems are compromised.
Takeaway 4: Supplement your resources
Having good, reliable partners in place who can come to your aid when you need it is priceless during a ransomware attack. Many organizations will have a 24/7 help desk, but they typically don’t have 24/7 server and network administrators, or security analysts.
Even during a cyber attack, when your systems are down, your staff is going to have to sleep at some point. Having pre-arranged support help cover additional shifts during a critical cyber event can help ensure your response and recovery aren’t slowed down.
Takeaway 5: Align on ransomware payment
In a ransomware incident, to pay or not to pay really is the question. Well in advance of an attack, internal cybersecurity stakeholders should create and align on the organization’s policy and plan around paying the ransom. Figuring that out during a ransomware incident is likely to result in unnecessary confusion and chaos.
Takeaway 6. Operationalize your system recovery process
After the ransomware attack, the hospital’s IT team faced an unexpected challenge. While the IT team had a pre-defined recovery order for the most critical systems, there were a lot of back-and-forth discussions around the order of recovery, and significant time spent putting the system recovery order together, and getting executive-level input and approval.
Had the order of system recovery been outlined in advance, with executive sign-off, communications and expectations around the recovery progress would have led to more productive progress.
Takeaway 7: Clarify your communication strategy
Ensure you have a well-defined, step-by-step communication strategy that extends throughout the entire organization, all the way to the executive level. Hospital staff will naturally seek updates and clarity about the ransomware situation and what lies ahead. While you may not have all the answers immediately, having a clear communication plan in place will help ensure staff, patients, and the community receive the support and reassurance they need during the challenging situation.
Resiliency after a ransomware attack
This real-life ransomware incident serves as a stark reminder of the critical importance of cybersecurity preparedness within hospitals and health systems. Proactive measures, such as comprehensive cybersecurity programs, cyber insurance coverage, and robust incident response planning, are vital to protect against the ever-evolving threats these organizations face.
To learn what steps the hospital took to recover from this ransomware attack, watch our on-demand webinar, From crisis to recovery: Lessons learned from a hospital’s ransomware attack.
Tamra Durfee is an experienced CISO with over 25 years in information security, compliance, regulatory risk, strategy, innovation, and technology transformation. For the past 8 years, she has specialized in healthcare cybersecurity and building risk-based medical device information security programs. She is a presenter at HIMSS, CHIME, CHA, and a healthcare security contributor to Healthcare IT News. Tamra holds certifications as a Certified Healthcare CIO (CHCIO), Certified Digital Healthcare Executive (CDH-E), GIAC Security Leadership Certification, Certified Professional in Healthcare Information Management Systems (CPHIMS), and IBM Certified Solutions Architect.